Thursday, December 18, 2008
Wednesday, September 10, 2008
Friday, August 29, 2008
Restoring Master and MSDB database in SQL Server
I don't need to mention the significance of Disaster Recovery (DR) plan for System and User Databases in SQL Server. I do test DR plan for User Database very often, but System Database generally I skip. In this post, I want to explain the DR plan and DR Plan testing for System databases. System database restoration is not as similar as User Database restoration. There are broadly three scenario where system database (Master and MSDB ) needs to be restored
(a) Master or MSDB to be restored from a earlier backup to undo the changes
(b) The Server machine crashed and sql server have been reinstalled with fresh copy.
(c) SQL Server is not starting because Master database corrupted
This scenario is well covered in this article
Proposed Backup Plan for System Databases
(a) Full Backup Daily
(b) If any major changes done like replication configuration or creation of Jobs take a backup of system databases after the configuration
You can either go for Hot Backup of Cold Backup of System databases. Hot backup is nothing but taking backup of system databases using BACKUP DATABASE T-SQL Command and you have to restore that backup using RESTORE DATABASE command. Hot backup is an online activity. Cold backup is stopping the SQL Server Engine , Copy MDF and LDF physical files to a backup location and Restart the service. Cold backup requires downtime and generally it is not the case in Production servers.
Scenario 1 : Restore Master & MSDB databases form the Backup file
I have full backup of Master and MSDB. My Master and MSDN databases got corrupted or i did some major changes and i want to rollback. Since i have backup i can restore the system database from the backup.
High level Steps
(a) Stop and Start the SQL Server Database Engine in Singe User Mode
(b) Restore the Master Database from SQLCMD prompt
(c) Start the SQL Server Database Engine
(d) Restore MSDB Database
Windows Start -- Run – Services.MSC --- Enter
You will get this window
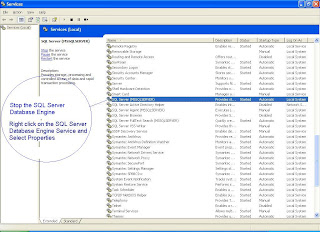
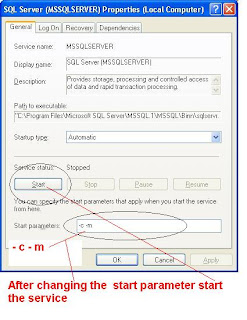
Restore the Master Database from Command Prompt
Windows --- Start --- Run --- CMD --- Enter
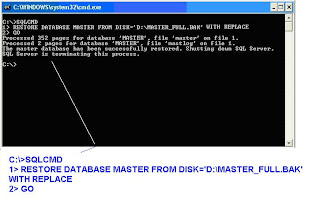
-- If the Screen is not readable this is the command and the result
C:\>SQLCMD
1> RESTORE DATABASE MASTER FROM DISK='D:\MASTER_FULL.BAK' WITH REPLACE
2> GO
Processed 352 pages for database 'MASTER', file 'master' on file 1.
Processed 2 pages for database 'MASTER', file 'mastlog' on file 1.
The master database has been successfully restored. Shutting down SQL Server.
SQL Server is terminating this process.
C:\>
The message says that you have successfully restored Master database.
Note : You have to restart the Database Engine Now
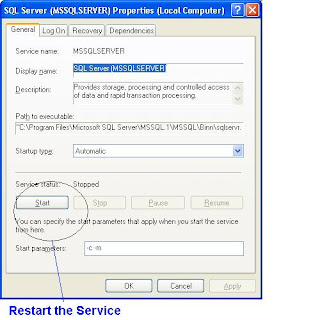
Restore MSDB Database from Management Studio
RESTORE DATABASE MSDB FROM DISK='D:\MSDB_FULL.BAK' WITH REPLACE
Scenario 2 : Server Crashes – Reinstalled SQL Server Instance
In this scenario, the important point is , you must build the new installation to the same build from where the backup was taken. You have to have same OS Version Edition, Service pack ,Patches and You also must have SQL Server Version , Edition , Service Pack and Patches as the Earlier server from where the backup was taken. Once you build your server to the same configuration the process is same as mentioned in Scenario 1
(a) Master or MSDB to be restored from a earlier backup to undo the changes
(b) The Server machine crashed and sql server have been reinstalled with fresh copy.
(c) SQL Server is not starting because Master database corrupted
This scenario is well covered in this article
Proposed Backup Plan for System Databases
(a) Full Backup Daily
(b) If any major changes done like replication configuration or creation of Jobs take a backup of system databases after the configuration
You can either go for Hot Backup of Cold Backup of System databases. Hot backup is nothing but taking backup of system databases using BACKUP DATABASE T-SQL Command and you have to restore that backup using RESTORE DATABASE command. Hot backup is an online activity. Cold backup is stopping the SQL Server Engine , Copy MDF and LDF physical files to a backup location and Restart the service. Cold backup requires downtime and generally it is not the case in Production servers.
Scenario 1 : Restore Master & MSDB databases form the Backup file
I have full backup of Master and MSDB. My Master and MSDN databases got corrupted or i did some major changes and i want to rollback. Since i have backup i can restore the system database from the backup.
High level Steps
(a) Stop and Start the SQL Server Database Engine in Singe User Mode
(b) Restore the Master Database from SQLCMD prompt
(c) Start the SQL Server Database Engine
(d) Restore MSDB Database
Windows Start -- Run – Services.MSC --- Enter
You will get this window


Restore the Master Database from Command Prompt
Windows --- Start --- Run --- CMD --- Enter

-- If the Screen is not readable this is the command and the result
C:\>SQLCMD
1> RESTORE DATABASE MASTER FROM DISK='D:\MASTER_FULL.BAK' WITH REPLACE
2> GO
Processed 352 pages for database 'MASTER', file 'master' on file 1.
Processed 2 pages for database 'MASTER', file 'mastlog' on file 1.
The master database has been successfully restored. Shutting down SQL Server.
SQL Server is terminating this process.
C:\>
The message says that you have successfully restored Master database.
Note : You have to restart the Database Engine Now

Restore MSDB Database from Management Studio
RESTORE DATABASE MSDB FROM DISK='D:\MSDB_FULL.BAK' WITH REPLACE
Scenario 2 : Server Crashes – Reinstalled SQL Server Instance
In this scenario, the important point is , you must build the new installation to the same build from where the backup was taken. You have to have same OS Version Edition, Service pack ,Patches and You also must have SQL Server Version , Edition , Service Pack and Patches as the Earlier server from where the backup was taken. Once you build your server to the same configuration the process is same as mentioned in Scenario 1
Labels:
FAQ
Thursday, August 28, 2008
Configuring Linked Server from SQL Server to MySQL
Recently I got a project in which there was a Migration Task to be done from MYSql to SQL Server. Prior to this I never worked in MySQL and I thought it would be just simple as creating LinkedServer to mySQL and pull the data to SQL Server from SQL Server itself. So I decided to create linked server from SQL Server to My SQL and pull the data using OPENQuery Function. I tried to configure linked server in SQL Server and then realized that it is not simple as that. I had to lot of steps like download driver, install it , configure the provider etc. As usual I searched in net and found a thread which neatly mentioned the steps ( SQLServerCentral.com). This thread really solved my problem in hours. Of course the thread was good enough for an expert (indirect way of saying that am an expert ), but for a newbie it may be bit confusing. So I thought to make a comprehensive document which has all the step by step screen shots so that the process will be easier. Having said that, I am not taking any credit for this document, the whole credit goes to Jim Dillon who posted his solution in the above mentioned site.
Tested Environment :
Operating System : Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows 2003
SQL Server : SQL Server 2005, (Note : I have not tested SQL Server 2000 but I feel it should work)
MySQL : MySQL Server 5.0
MySQL ODBC : ODBC 3.51
High level Steps
• Download and Install ODBC Driver from MYSQL Site
• Create ODBC DSN
• Create Linked Server in SQL Server
• Configure Provider
• Create linked server
• Enable OpenQuery in SQL Server instance
• Create Openquery script
Step 1 : Download MySQL ODBC Connector
Download MySQL Connector/ODBC 3.51 from : http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/3.51.html
Download the ODBC connector for your Operating System. I have windows xp , so I will download Windows MSI installer (x86)
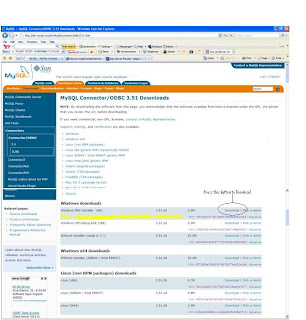
Step 2 : Install ODBC connector
Double click the downloaded file
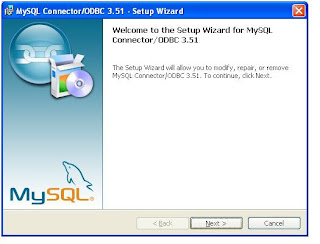
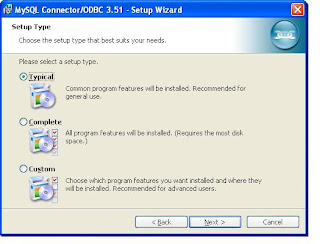
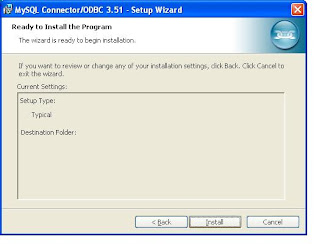
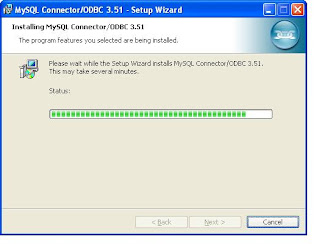
At last screen you will get a Finish button and click that. Now You have installed ODBC connector for MySQL.
Step 3 : Create System DSN for MYSql ODBC Driver
Windows Start --- >> Run --- >> odbcad32
Or
Windows Start --- >> Control Panel ->Performance and Maintenance (in XP) --- >> Administrative Tools -> Data Sources (ODBC)
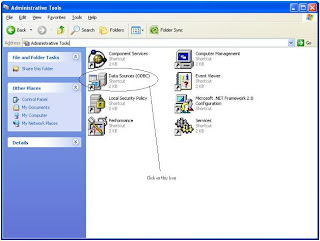
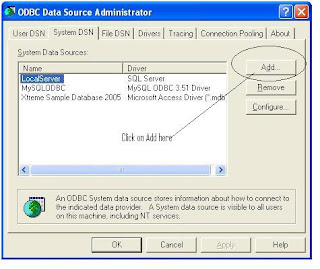
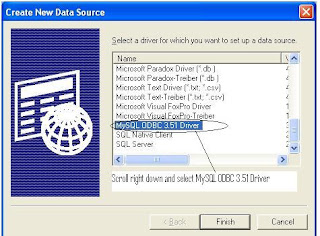
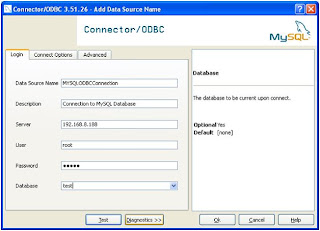
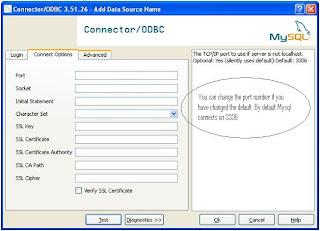
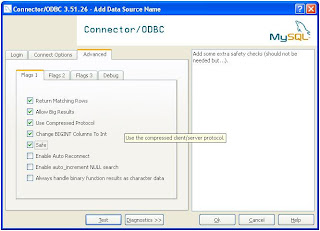
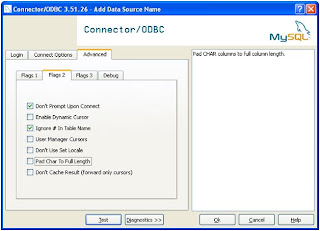
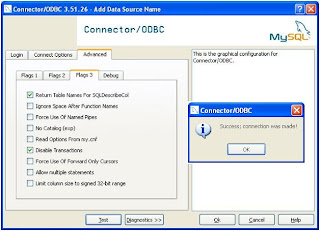
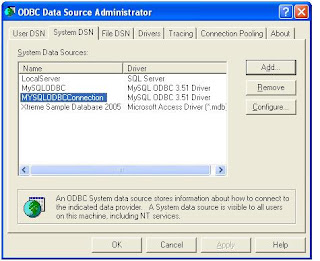
Step 3 : Create Linked Server in SQL Server 2005.
Change the properties of the Provider
Select the properties as shown in the screens
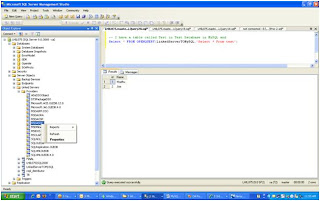
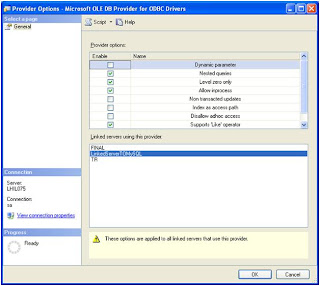
--======================================================================================================
Script to Create Linked Server
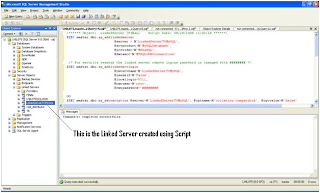
It is always better to create linked server using Script than GUI. You have more control and script of course is more readable. I am not giving the screen shot for this steps. Copy paste the script to a query analyzer change DSN Name, Username, Password and run.
--======================================================================================================
/****** Object: LinkedServer [LinkedServerTOMySQL] Script Date: 08/28/2008 11:40:28 ******/
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'LinkedServerTOMySQL',
@srvproduct=N'MySQLDatabase',
@provider=N'MSDASQL',
@datasrc=N'MYSQLODBCConnection'
Parameter Explanation
@server = N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', -- Linked server name (it can be anything)
@srvproduct=N'MySQLDatabase', -- Keep as it is
@provider=N'MSDASQL', -- Keep as it is
@datasrc=N'MYSQLODBCConnection' --DSN Name Created in Step 3 (very important)
/* For security reasons the linked server remote logins password is changed with ######## */
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL',
@useself=N'False',
@locallogin=NULL,
@rmtuser=N'root',
@rmtpassword='change thepasswordhere'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'collation compatible', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'data access', @optvalue=N'true'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'dist', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'pub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'rpc', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'rpc out', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'sub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'connect timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'collation name', @optvalue=null
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'lazy schema validation', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'query timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'use remote collation', @optvalue=N'true'
--======================================================================================================
Enable Distributed Queries (OpenQuery) in SQL Instance
By default in SQL Server 2005 Distributed Queries are disabled. You have to enable it using the following script. (Note : In SQL Server 2000 no need to run this script)
Copy this script to a query analyzer and run
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'show advanced options', N'1' RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', N'1'
RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
Finally, Test the Linked Server and Run a OpenQuer against the LinkedServer Configured
Check the following Screen
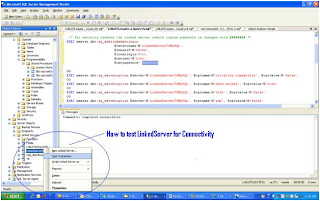
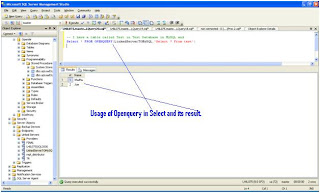
Restart Database Engine and SQL Server Agent
Once you have completed all the steps you may restart the services. I have not tested this whether you need to restart it or not
Summary :
If anyone feels some screen shots are missing please drop a comment.
Tested Environment :
Operating System : Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows 2003
SQL Server : SQL Server 2005, (Note : I have not tested SQL Server 2000 but I feel it should work)
MySQL : MySQL Server 5.0
MySQL ODBC : ODBC 3.51
High level Steps
• Download and Install ODBC Driver from MYSQL Site
• Create ODBC DSN
• Create Linked Server in SQL Server
• Configure Provider
• Create linked server
• Enable OpenQuery in SQL Server instance
• Create Openquery script
Step 1 : Download MySQL ODBC Connector
Download MySQL Connector/ODBC 3.51 from : http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/odbc/3.51.html
Download the ODBC connector for your Operating System. I have windows xp , so I will download Windows MSI installer (x86)

Step 2 : Install ODBC connector
Double click the downloaded file




At last screen you will get a Finish button and click that. Now You have installed ODBC connector for MySQL.
Step 3 : Create System DSN for MYSql ODBC Driver
Windows Start --- >> Run --- >> odbcad32
Or
Windows Start --- >> Control Panel ->Performance and Maintenance (in XP) --- >> Administrative Tools -> Data Sources (ODBC)









Step 3 : Create Linked Server in SQL Server 2005.
Change the properties of the Provider
Select the properties as shown in the screens



--======================================================================================================
Script to Create Linked Server
It is always better to create linked server using Script than GUI. You have more control and script of course is more readable. I am not giving the screen shot for this steps. Copy paste the script to a query analyzer change DSN Name, Username, Password and run.
--======================================================================================================
/****** Object: LinkedServer [LinkedServerTOMySQL] Script Date: 08/28/2008 11:40:28 ******/
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver
@server = N'LinkedServerTOMySQL',
@srvproduct=N'MySQLDatabase',
@provider=N'MSDASQL',
@datasrc=N'MYSQLODBCConnection'
Parameter Explanation
@server = N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', -- Linked server name (it can be anything)
@srvproduct=N'MySQLDatabase', -- Keep as it is
@provider=N'MSDASQL', -- Keep as it is
@datasrc=N'MYSQLODBCConnection' --DSN Name Created in Step 3 (very important)
/* For security reasons the linked server remote logins password is changed with ######## */
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedsrvlogin
@rmtsrvname=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL',
@useself=N'False',
@locallogin=NULL,
@rmtuser=N'root',
@rmtpassword='change thepasswordhere'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'collation compatible', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'data access', @optvalue=N'true'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'dist', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'pub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'rpc', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'rpc out', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'sub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'connect timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'collation name', @optvalue=null
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'lazy schema validation', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'query timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'LinkedServerTOMySQL', @optname=N'use remote collation', @optvalue=N'true'
--======================================================================================================
Enable Distributed Queries (OpenQuery) in SQL Instance
By default in SQL Server 2005 Distributed Queries are disabled. You have to enable it using the following script. (Note : In SQL Server 2000 no need to run this script)
Copy this script to a query analyzer and run
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'show advanced options', N'1' RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
EXEC sys.sp_configure N'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', N'1'
RECONFIGURE WITH OVERRIDE
Finally, Test the Linked Server and Run a OpenQuer against the LinkedServer Configured
Check the following Screen


Restart Database Engine and SQL Server Agent
Once you have completed all the steps you may restart the services. I have not tested this whether you need to restart it or not
Summary :
If anyone feels some screen shots are missing please drop a comment.
Labels:
FAQ
Saturday, August 9, 2008
Creating Files from the images stored in Binary format in the database table.
Problem :-
Images are stored in a database table-Varbinary (SQL Server 2005) column. Form the stored images we need to create individual image files.
Solution :
BCP QUERYOUT with little format file tweaking can be a wonderful solution for this. You can include this BCP queryout in a XP_CMDShell dynamic sql from SQL Env and it will provide a simple solution to this complex requirement.
Demo environment details
Database : AdventureWorks
Table : ProductionPhoto
Image Column : LargePhoto
There are 101 rows in this table, each one having a LargePhoto column with some image. We need to create 101 JPG files from this table. Here we go…
Step 1 : Creation of Format File
C:\>bcp AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto format nul -T -n -f c:\PP.fmt
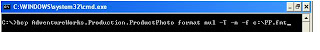
Step 2 : Format file will looks something like this
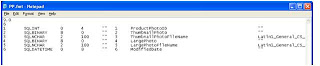
Step 3 : Tweak Format file : We need to get the LargePhoto column binary data.
• Remove all column except LargePhoto
• Change Prefix of LargePhoto column from 8 to 0 (zero)
• Change Number of column from 6 to 1
• Change column sequence from 4 to 1
• After the ncessary modification the format file should look like next sceen
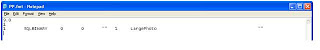
Step 4 : Use BCP QUERYOUT to create Image files
My BCP QUERYOUT query is this
--=====================================================================================
C:\>bcp "SELECT top 1 LargePhoto FROM AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto wh
ere ProductPhotoID=69" queryout c:\ProductPhotoID_69.jpg -T -fC:\PP.fmt
Starting copy...
1 rows copied.
Network packet size (bytes): 4096
Clock Time (ms.) Total : 1 Average : (1000.00 rows per sec.)
C:\>
=====================================================================================
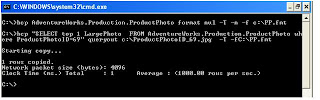
The above BCP Queryout statement is created a file ProductPhotoID_69.jpg . Now let us go and open that form windows
Double click the file and the file opened
Step 5 : Loop through all the records in this table and create respective files of each row in C:\Photo folder
--==============================================================================
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @ProductPhotoID int, @Sqlstmt varchar(4000),@LargePhotoFileName varchar(200)
DECLARE Cursor_ProductPhoto CURSOR FOR
SELECT ProductPhotoID, LargePhotoFileName
from AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto
ORDER BY ProductPhotoID
OPEN Cursor_ProductPhoto
FETCH NEXT FROM Cursor_ProductPhoto
INTO @ProductPhotoID, @LargePhotoFileName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
PRINT @LargePhotoFileName
-- Framing DynamicSQL for XP_CMDshell
Set @Sqlstmt='bcp "SELECT top 1 LargePhoto FROM AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto where ProductPhotoID='+str(@ProductPhotoID)+'" queryout c:\Photo\'+ltrim(@LargePhotoFileName)+' -T -fC:\PP.fmt'
print @sqlstmt
exec xp_cmdshell @sqlstmt
FETCH NEXT FROM Cursor_ProductPhoto
INTO @ProductPhotoID, @LargePhotoFileName
END
CLOSE Cursor_ProductPhoto
DEALLOCATE Cursor_ProductPhoto
--==============================================================================
Check this Screen. The above script has created individual files in this folder
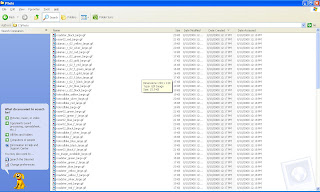
Summary :-
This solution provides very simple method to create files from the binary stored in Database by little tweaking in Format file. If you want to keep a backup of Images in file system format then this method can really help.
Images are stored in a database table-Varbinary (SQL Server 2005) column. Form the stored images we need to create individual image files.
Solution :
BCP QUERYOUT with little format file tweaking can be a wonderful solution for this. You can include this BCP queryout in a XP_CMDShell dynamic sql from SQL Env and it will provide a simple solution to this complex requirement.
Demo environment details
Database : AdventureWorks
Table : ProductionPhoto
Image Column : LargePhoto
There are 101 rows in this table, each one having a LargePhoto column with some image. We need to create 101 JPG files from this table. Here we go…
Step 1 : Creation of Format File
C:\>bcp AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto format nul -T -n -f c:\PP.fmt

Step 2 : Format file will looks something like this

Step 3 : Tweak Format file : We need to get the LargePhoto column binary data.
• Remove all column except LargePhoto
• Change Prefix of LargePhoto column from 8 to 0 (zero)
• Change Number of column from 6 to 1
• Change column sequence from 4 to 1
• After the ncessary modification the format file should look like next sceen

Step 4 : Use BCP QUERYOUT to create Image files
My BCP QUERYOUT query is this
--=====================================================================================
C:\>bcp "SELECT top 1 LargePhoto FROM AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto wh
ere ProductPhotoID=69" queryout c:\ProductPhotoID_69.jpg -T -fC:\PP.fmt
Starting copy...
1 rows copied.
Network packet size (bytes): 4096
Clock Time (ms.) Total : 1 Average : (1000.00 rows per sec.)
C:\>
=====================================================================================

The above BCP Queryout statement is created a file ProductPhotoID_69.jpg . Now let us go and open that form windows

Double click the file and the file opened

Step 5 : Loop through all the records in this table and create respective files of each row in C:\Photo folder
--==============================================================================
SET NOCOUNT ON
DECLARE @ProductPhotoID int, @Sqlstmt varchar(4000),@LargePhotoFileName varchar(200)
DECLARE Cursor_ProductPhoto CURSOR FOR
SELECT ProductPhotoID, LargePhotoFileName
from AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto
ORDER BY ProductPhotoID
OPEN Cursor_ProductPhoto
FETCH NEXT FROM Cursor_ProductPhoto
INTO @ProductPhotoID, @LargePhotoFileName
WHILE @@FETCH_STATUS = 0
BEGIN
PRINT @LargePhotoFileName
-- Framing DynamicSQL for XP_CMDshell
Set @Sqlstmt='bcp "SELECT top 1 LargePhoto FROM AdventureWorks.Production.ProductPhoto where ProductPhotoID='+str(@ProductPhotoID)+'" queryout c:\Photo\'+ltrim(@LargePhotoFileName)+' -T -fC:\PP.fmt'
print @sqlstmt
exec xp_cmdshell @sqlstmt
FETCH NEXT FROM Cursor_ProductPhoto
INTO @ProductPhotoID, @LargePhotoFileName
END
CLOSE Cursor_ProductPhoto
DEALLOCATE Cursor_ProductPhoto
--==============================================================================
Check this Screen. The above script has created individual files in this folder

Summary :-
This solution provides very simple method to create files from the binary stored in Database by little tweaking in Format file. If you want to keep a backup of Images in file system format then this method can really help.
Wednesday, August 6, 2008
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Released
Finally Microsoft SQL Server 2008 RTM version is released today. It was suppose to release almost one year back but somehow did not. There are seven editions in SQL Server 2008.
In a press release, Microsoft cited several large enterprise customers who are testing SQL Server 2008, including Xerox, Siemens, Clear Channel Communications and Fidelity Investments.
In a press release, Microsoft cited several large enterprise customers who are testing SQL Server 2008, including Xerox, Siemens, Clear Channel Communications and Fidelity Investments.
Thursday, July 24, 2008
Best Practices, Design and Development Guidelines for SQL Server
There are many resources available in the net but here I have a list of Best Practices,Design Guidelines and General Guidelines in Database Development and Designing specifically for SQL Server.
Best Practices
1. Use Stored Procedure: Benefits are as follows :-
(a) Code reusability
(b) Security : You can control permission on sp
(c) Execution plan reusability : Though adhoc query also create and reuse plan, the plan is reused only when the query is textual match and the datatypes are matching with the previous call. Any datatype or you have an extra space in the query then new plan is created
Eg.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Select Sal from Employee where sal=$10 --Money
--And
Select Sal from Employee where sal=10 -- Int
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Above statements will create different execution plan because the datatype of value is different.
(d) Procedure gives more Readability and Manageability.
2. Use Fully Qualified Name for objects : This is very significant. You must use fully qualified name when you refer any object in SQL Server. Ie. SchemaName.ObjectName. Because, when the execution plan is prepared by the query engine , in the binding process, Query engine has to resolve the Object existence. If you specify the fully qualified name the object resolution become easy for the engine and also it will be more readable.
3. Avoid using Scalar Function in SELECT statement: Recently I faced this issue and I emphasis this point. Never use Scalar function inside a query which returns a large number of rows. Scalar function behave like a cursor when you use Scalar function inside a query which returns large number of rows . Change the scalar function to Inline or Multiline table function or a view.
4. Avoid Mixing-up DML and DDL statement on a temp table inside sp : This is very important. When you Create a temptable (#table) and ALTER the same temptable in the same storedprocedure later, this DDL and DML mix-up causes the stored procedure to get recompiled. So, if a stored procedure is getting recompiled in each call check this point.
5. Select only the required columns: Select only the required column in select statement. Usage of SELECT * can be the cause of NOT using the indexes available on the table . Also if you are selecting more data then you are doing more IO. In short we should limit the IO.
6. Avoid Usage of HINTS : HINTS prevent Query engine automated optimization capability. You may find a hint gives you better performance on a particular scenario. But it may behave differently as the data grows or when scenario changes. Check this KB on HINTS http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms187713.aspx
7. Use Table variable and Temp table as far as possible: You must use Table variable (@TableName) or Temp table (#TableName) for intermediate storage of records in an procedure. Avoid using Table variable for large record set. There are pros and cons between Table variable and Temp table, but in general, if the record set is small you should go for Table variable.
8. Use SET NOCOUNT ON : Basically, you must reduce the data transferred on the network. Database Engine, return the number of rows effected by the statements to the client which is unnecessary and you can avoid that using this statement. It is a must in all Stored procedure.
9. Do not change SET OPTION In connection: Changing SET Option during connection or anywhere else will cause the stored procedure to recompile. Refer this KB for more info http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/sql/2005/recomp.mspx
10. EXISTS vs IN : IN Operator can easily be replaced by EXISTS which is more optimized for correlated queries. But you may find IN better for small tables.
11. Keep the transaction as short as possible: Deadlock is a outcome of ill-formed query. You must keep the transaction as short as possible to avoid dead lock. And also refer the object in the same order inside transaction.
12. Avoid user input inside a transaction: Do not accept a user input inside a transaction.
13. Avoid doing Front-End work in Databases : String processing , Ordering , Conversion etc can easily be done at the client side and you should avoid doing these kind of work in Database. The point here is, you should have a clear segregation of tasks between Data Layer, Data Access Layer (DAL) and Business Layer. For example, you can easily number your rows in client side where as if you do that in Database you have to use a Function or extra join which can be avoided.
14. Avoid Function in select statement: Any functions like CONVERT(),CAST,ISNULL usage in query may ignore the indexes available on the table.
15. Do not use EXEC (‘String’) , use sp_executeSql : As far as possible you try to avoid Dynamic SQL. If there is no other option use sp_ExecuteSQL DO NOT USE EXEC(‘string’). Because EXEC statement is prone to SQL Injection and it is not parametrized query which can re-use execution plan.
16. Use proper size for the input parameter: This is one of the step to avoid SQL Injection and also the reduce the memory usage.
17. Do not keep the name of sp with sp_ prefix: Naming convention is very important. Do not name the storedprocedures with SP_ as prefix (eg sp_ somespname ) because this naming convention is used for system stored procedure in MS SQL Server.
18. USE WHERE Condition as far as possible: Basically, you should limit the rows fetched by the query.
19. Avoid Negative operator : Avoid using <> , NOT IN, NOT EXISTS kind of operator because it causes a table scan. Query engine has to ensure there is not data till the last row is read.
20. Avoid Cursor /loops: In SET Based operation, in general looping can be avoided.
21. Avoid using Like ‘% %’ : If you use % in both side of the searching value, the query will go for table scan which should be avoided. If the application is more text searching kind go for Full Text Index.
22. Do not use WITH Recompile : Usage of WITH Recompile causes the procedure to recompile each time it call. You must avoid this command.
23. JOIN Consideration : When you JOIN two table consider these points
(a) Avoid using negative operator (<> ,NOT IN) in JOIN
(b) Avoid Like operator in Join
Design Guidelines
1. Create Covering indexes: Create covering indexes. Covering index will have all the data required by the query at the leaf level itself. Covering contains all the columns used in SELECT, WHERE, ORDERBY, JOIN etc.
Eg.
Select Col1,Col2 From YourTableName Where Col3=1 Order by Col4.
The coveing index for the above mentioned query will be
Col1+ col2+ col3+ col4. (Note : Most selective column should come first in the index creation statement)
2. Remove Unwanted indexes : In SQL Server 2005 it is very easy to find unused indexes. Too many or too less indexes on a table are equally bad. If you have unwanted/unused indexes on a table Insert/Update statement will have performance hit and also we all know indexes consume space.
3. Create the indexes most selective column as first column in Index : Index creation has to be done after proper analysis. You must create the index with Most Selective column at first and so on.
4. Formatting the stored procedure and queries : You must have a format / template for each object (sp/function/views) and everyone (the dev team) should stick to the format defined. And also the query has to be formatted well so that it is more readable.
5. Use Identity column if the table is INSERT oriented table as Clustered Index to avoid page split : This is a design and data modeling issue. If you have more insert kind of table (some kind of logging table) then you must go for Identity Column (ever increasing) as Clustered Index. This helps to resolve page split. There may be Hotspot issue (all transaction contending for same page of a table), but I have never faced.
6. Use proper fillfactor for Indexes: Very important to avoid Page Split. In general transactional table can be kept at 80-90 fillfactor.
7. Balanced Normalization / De-normalization: You must have a trade off between Normalization and de-normalization. At time De-normalization can give you better performance at the cost of Data redundancy.
8. Primary Key size and Composite primary key : You must limit the size of the PK because, in a relational database, you may be creating foreign key which refers this primary key. If you have multiple Column in PK (composite PK) or big size , you are knowingly or unknowingly increasing the space usage. If the composite PK contains more than 3 columns then you may go for surrogate key like Identity column as PK.
9. Do not alter system Objects: If your application requires some tweaking of system objects then you are in trouble. The structure of system object can be changed by Microsoft in any release or patches. So avoid such modeling.
Guidelines for Datatype Selection
As a Database architect I believe in the significance of proper datatype selection while designing the tables. if you do a proper analysis of the data and then select the datatype, then you can control the row, page, table size and hence increase the overall performance of the database. Following points you may consider when you design a table :-
1. If your database is to support web-based application better to go for UNICODE for the scalability of the application. (Unicode (nchar, nvarchar) takes 2 bytes per char where as ASCII (char,varchar) datatypes takes 1 bytes per char)
2. If your application is multi-lingual go for UNICODE.
3. If you are planning to include CLRDatatype (SQL Server 2005) in the database go for UNICODE Datatypes , because, if CLRDatatype is going to consume the data then it must be in UNICODE.
4. For numeric column, find the range that column is going to have and then choose the datatype. For eg. You have a table called Department and DepartmentID is the Primarykey Column. You know that the maximum rows in this table is 20-30. In such cases it is recommended to choose TinyINT datatype for this column. Generally keeping all numeric columns type of INT without analyzing the range that column going to support is not at all recommended from storage perspective.
5. Description /Comments /Remarks sort of columns may or may not have data for all the rows. So it is better to go for Variable datatypes like Varchar ,Nvarchar.
6. If you know the column is not nullable and it may contain more or less the same size of the data then for sure go for Fixed datatype like CHAR or NCHAR. Having said that it is important to know that, if you select fixed datatypes and if the column is nullable then, if you do not have any data (null) then also the column will consume the space.
7. If the size of the column is less than 20 char , use fixed width datatypes like NCHAR or CHAR.
8. I have seen in many applications use Decimal to store currency kind of data though the application needs the precision which can be supported by money. So, my point here is, use Money datatype if you need only 4 precision.
9. Use UniqueIdentitifier column as PK and ClusteredIndex or so only when it is unavoidable because UniqueIdentitifier takes 16 Bytes of the space.
General Guidelines
1. Write ANSI standard Code : You must write standard code which will scale your application. ie migration to next version will not be an issue. Do not use Deprecated features. For eg. There are DBCC Command to rebuild index but in SQL Server 2005 in order to standardize things, you have ALTER INDEX command which does the same thing.
2. Do not give Error message which expose your architecture to the frontend: I have seen folks giving very detailed error message which tells you “ blah blah table do not have this rows in blah blah database” kind which can be a invitation to the hacker
3. Use proper Isolation level required for the application: This is very significant. Before going for any isolation level, you must know the implication. All application cannot afford READUNCOMMITTED Isolation level since it can cause data inconsistency issues like Dirty Read, Phantom read, Lost Update etc. WITH NOLOCK Hint is nothing but READ UNCOMMITTED isolation level.
4. Keep the Database Object Scripts in Source Control: We all are aware of this point but generally ignore. This is important for fault tolerance and management when multiple developers are working on same project.
Best Practices
1. Use Stored Procedure: Benefits are as follows :-
(a) Code reusability
(b) Security : You can control permission on sp
(c) Execution plan reusability : Though adhoc query also create and reuse plan, the plan is reused only when the query is textual match and the datatypes are matching with the previous call. Any datatype or you have an extra space in the query then new plan is created
Eg.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Select Sal from Employee where sal=$10 --Money
--And
Select Sal from Employee where sal=10 -- Int
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Above statements will create different execution plan because the datatype of value is different.
(d) Procedure gives more Readability and Manageability.
2. Use Fully Qualified Name for objects : This is very significant. You must use fully qualified name when you refer any object in SQL Server. Ie. SchemaName.ObjectName. Because, when the execution plan is prepared by the query engine , in the binding process, Query engine has to resolve the Object existence. If you specify the fully qualified name the object resolution become easy for the engine and also it will be more readable.
3. Avoid using Scalar Function in SELECT statement: Recently I faced this issue and I emphasis this point. Never use Scalar function inside a query which returns a large number of rows. Scalar function behave like a cursor when you use Scalar function inside a query which returns large number of rows . Change the scalar function to Inline or Multiline table function or a view.
4. Avoid Mixing-up DML and DDL statement on a temp table inside sp : This is very important. When you Create a temptable (#table) and ALTER the same temptable in the same storedprocedure later, this DDL and DML mix-up causes the stored procedure to get recompiled. So, if a stored procedure is getting recompiled in each call check this point.
5. Select only the required columns: Select only the required column in select statement. Usage of SELECT * can be the cause of NOT using the indexes available on the table . Also if you are selecting more data then you are doing more IO. In short we should limit the IO.
6. Avoid Usage of HINTS : HINTS prevent Query engine automated optimization capability. You may find a hint gives you better performance on a particular scenario. But it may behave differently as the data grows or when scenario changes. Check this KB on HINTS http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms187713.aspx
7. Use Table variable and Temp table as far as possible: You must use Table variable (@TableName) or Temp table (#TableName) for intermediate storage of records in an procedure. Avoid using Table variable for large record set. There are pros and cons between Table variable and Temp table, but in general, if the record set is small you should go for Table variable.
8. Use SET NOCOUNT ON : Basically, you must reduce the data transferred on the network. Database Engine, return the number of rows effected by the statements to the client which is unnecessary and you can avoid that using this statement. It is a must in all Stored procedure.
9. Do not change SET OPTION In connection: Changing SET Option during connection or anywhere else will cause the stored procedure to recompile. Refer this KB for more info http://www.microsoft.com/technet/prodtechnol/sql/2005/recomp.mspx
10. EXISTS vs IN : IN Operator can easily be replaced by EXISTS which is more optimized for correlated queries. But you may find IN better for small tables.
11. Keep the transaction as short as possible: Deadlock is a outcome of ill-formed query. You must keep the transaction as short as possible to avoid dead lock. And also refer the object in the same order inside transaction.
12. Avoid user input inside a transaction: Do not accept a user input inside a transaction.
13. Avoid doing Front-End work in Databases : String processing , Ordering , Conversion etc can easily be done at the client side and you should avoid doing these kind of work in Database. The point here is, you should have a clear segregation of tasks between Data Layer, Data Access Layer (DAL) and Business Layer. For example, you can easily number your rows in client side where as if you do that in Database you have to use a Function or extra join which can be avoided.
14. Avoid Function in select statement: Any functions like CONVERT(),CAST,ISNULL usage in query may ignore the indexes available on the table.
15. Do not use EXEC (‘String’) , use sp_executeSql : As far as possible you try to avoid Dynamic SQL. If there is no other option use sp_ExecuteSQL DO NOT USE EXEC(‘string’). Because EXEC statement is prone to SQL Injection and it is not parametrized query which can re-use execution plan.
16. Use proper size for the input parameter: This is one of the step to avoid SQL Injection and also the reduce the memory usage.
17. Do not keep the name of sp with sp_ prefix: Naming convention is very important. Do not name the storedprocedures with SP_ as prefix (eg sp_ somespname ) because this naming convention is used for system stored procedure in MS SQL Server.
18. USE WHERE Condition as far as possible: Basically, you should limit the rows fetched by the query.
19. Avoid Negative operator : Avoid using <> , NOT IN, NOT EXISTS kind of operator because it causes a table scan. Query engine has to ensure there is not data till the last row is read.
20. Avoid Cursor /loops: In SET Based operation, in general looping can be avoided.
21. Avoid using Like ‘% %’ : If you use % in both side of the searching value, the query will go for table scan which should be avoided. If the application is more text searching kind go for Full Text Index.
22. Do not use WITH Recompile : Usage of WITH Recompile causes the procedure to recompile each time it call. You must avoid this command.
23. JOIN Consideration : When you JOIN two table consider these points
(a) Avoid using negative operator (<> ,NOT IN) in JOIN
(b) Avoid Like operator in Join
Design Guidelines
1. Create Covering indexes: Create covering indexes. Covering index will have all the data required by the query at the leaf level itself. Covering contains all the columns used in SELECT, WHERE, ORDERBY, JOIN etc.
Eg.
Select Col1,Col2 From YourTableName Where Col3=1 Order by Col4.
The coveing index for the above mentioned query will be
Col1+ col2+ col3+ col4. (Note : Most selective column should come first in the index creation statement)
2. Remove Unwanted indexes : In SQL Server 2005 it is very easy to find unused indexes. Too many or too less indexes on a table are equally bad. If you have unwanted/unused indexes on a table Insert/Update statement will have performance hit and also we all know indexes consume space.
3. Create the indexes most selective column as first column in Index : Index creation has to be done after proper analysis. You must create the index with Most Selective column at first and so on.
4. Formatting the stored procedure and queries : You must have a format / template for each object (sp/function/views) and everyone (the dev team) should stick to the format defined. And also the query has to be formatted well so that it is more readable.
5. Use Identity column if the table is INSERT oriented table as Clustered Index to avoid page split : This is a design and data modeling issue. If you have more insert kind of table (some kind of logging table) then you must go for Identity Column (ever increasing) as Clustered Index. This helps to resolve page split. There may be Hotspot issue (all transaction contending for same page of a table), but I have never faced.
6. Use proper fillfactor for Indexes: Very important to avoid Page Split. In general transactional table can be kept at 80-90 fillfactor.
7. Balanced Normalization / De-normalization: You must have a trade off between Normalization and de-normalization. At time De-normalization can give you better performance at the cost of Data redundancy.
8. Primary Key size and Composite primary key : You must limit the size of the PK because, in a relational database, you may be creating foreign key which refers this primary key. If you have multiple Column in PK (composite PK) or big size , you are knowingly or unknowingly increasing the space usage. If the composite PK contains more than 3 columns then you may go for surrogate key like Identity column as PK.
9. Do not alter system Objects: If your application requires some tweaking of system objects then you are in trouble. The structure of system object can be changed by Microsoft in any release or patches. So avoid such modeling.
Guidelines for Datatype Selection
As a Database architect I believe in the significance of proper datatype selection while designing the tables. if you do a proper analysis of the data and then select the datatype, then you can control the row, page, table size and hence increase the overall performance of the database. Following points you may consider when you design a table :-
1. If your database is to support web-based application better to go for UNICODE for the scalability of the application. (Unicode (nchar, nvarchar) takes 2 bytes per char where as ASCII (char,varchar) datatypes takes 1 bytes per char)
2. If your application is multi-lingual go for UNICODE.
3. If you are planning to include CLRDatatype (SQL Server 2005) in the database go for UNICODE Datatypes , because, if CLRDatatype is going to consume the data then it must be in UNICODE.
4. For numeric column, find the range that column is going to have and then choose the datatype. For eg. You have a table called Department and DepartmentID is the Primarykey Column. You know that the maximum rows in this table is 20-30. In such cases it is recommended to choose TinyINT datatype for this column. Generally keeping all numeric columns type of INT without analyzing the range that column going to support is not at all recommended from storage perspective.
5. Description /Comments /Remarks sort of columns may or may not have data for all the rows. So it is better to go for Variable datatypes like Varchar ,Nvarchar.
6. If you know the column is not nullable and it may contain more or less the same size of the data then for sure go for Fixed datatype like CHAR or NCHAR. Having said that it is important to know that, if you select fixed datatypes and if the column is nullable then, if you do not have any data (null) then also the column will consume the space.
7. If the size of the column is less than 20 char , use fixed width datatypes like NCHAR or CHAR.
8. I have seen in many applications use Decimal to store currency kind of data though the application needs the precision which can be supported by money. So, my point here is, use Money datatype if you need only 4 precision.
9. Use UniqueIdentitifier column as PK and ClusteredIndex or so only when it is unavoidable because UniqueIdentitifier takes 16 Bytes of the space.
General Guidelines
1. Write ANSI standard Code : You must write standard code which will scale your application. ie migration to next version will not be an issue. Do not use Deprecated features. For eg. There are DBCC Command to rebuild index but in SQL Server 2005 in order to standardize things, you have ALTER INDEX command which does the same thing.
2. Do not give Error message which expose your architecture to the frontend: I have seen folks giving very detailed error message which tells you “ blah blah table do not have this rows in blah blah database” kind which can be a invitation to the hacker
3. Use proper Isolation level required for the application: This is very significant. Before going for any isolation level, you must know the implication. All application cannot afford READUNCOMMITTED Isolation level since it can cause data inconsistency issues like Dirty Read, Phantom read, Lost Update etc. WITH NOLOCK Hint is nothing but READ UNCOMMITTED isolation level.
4. Keep the Database Object Scripts in Source Control: We all are aware of this point but generally ignore. This is important for fault tolerance and management when multiple developers are working on same project.
Monday, July 21, 2008
Visio - ERROR – Failed to Initialize the Modeling Engine.
Recently I reinstalled Visio 2003 Enterprise Architecture edition and it started popping up the above mentioned error. I was not able to do any Database modeling kind of tasks since the options were not available. I goggled as usual and I found the same issue is being reported by many. The solution for this issue is uninstalling Visio Update patch KB947650. I did the same and it fixed my error
follow these steps :-
Control Panel –
Add or Remove Programs
Check “ Show Updates” check box in Add or Remove programs window
– MS Visio Enterprise Architect
Select KB947650 update and remove it.
follow these steps :-
Control Panel –
Add or Remove Programs
Check “ Show Updates” check box in Add or Remove programs window
– MS Visio Enterprise Architect
Select KB947650 update and remove it.
Tuesday, July 15, 2008
Scalar Function and Performance Issue
Performance tuning is one of the main tasks I do and there is always scope to learn new things in this area. Recently, I got a query which was using a Scalar function takes almost 4 min. When the scalar function is removed it came within one sec. I know scalar function inside a query is not optimized and may be because of that I very rarely use scalar function. But in this particular project, scalar function is very common and tuning query with scalar function is little tricky. Following are the suggestions I got from my MVP friends :-
(a) If possible create a view and join with the view: This was not possible for me since I had to pass the parameter.
(b) You may also create a Inline or multiline table function: I went with this route. I created a multiline function and I tell you the performance was improved manifold.
Sample code
The scalar function was something like returning appointments concatenated string for a given EmployeeID
Same logic in Multiline function which uses FOR XML PATH query
Create function fnConcatMultipleRowValuesToColumn ()
Returns @tab Table (EmpID int,con varchar(200))
As
Begin
DECLARE @Designation TABLE (EmpID INT, Code VARCHAR(50))
INSERT @Designation
SELECT 100, 'SR. Engr.' UNION ALL
SELECT 100, 'TL' UNION ALL
SELECT 100, 'PM' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'QA' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'SR QA' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'TL QA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'DBA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'SR. DBA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'TL DBA'
-- Show the expected output
Insert @tab
SELECT DISTINCT s1.EmpID,
STUFF((SELECT DISTINCT TOP 100 PERCENT ',' + s2.CODE FROM @Designation AS s2
WHERE s2.EmpID = s1.EmpID ORDER BY ',' + s2.CODE FOR XML PATH('')), 1, 1, '') AS CODES
FROM @Designation AS s1
ORDER BY s1.EmpID
Return
End
Function Call
Select *From fnConcatMultipleRowValuesToColumn ()
Summary :
Avoid Scalar functions as far as possible. This was introduced in SQL Server 2000 and there may be certain scenario where it may be useful like encapsulation. But when you use scalar function within a select statement which returns many rows may trouble you.
Few good resources to refer
http://sqlblog.com/blogs/adam_machanic/archive/2006/08/04/scalar-functions-inlining-and-performance-an-entertaining-title-for-a-boring-post.aspx
http://www.sqlservercentral.com/Forums/Topic446308-360-1.aspx
(a) If possible create a view and join with the view: This was not possible for me since I had to pass the parameter.
(b) You may also create a Inline or multiline table function: I went with this route. I created a multiline function and I tell you the performance was improved manifold.
Sample code
The scalar function was something like returning appointments concatenated string for a given EmployeeID
Same logic in Multiline function which uses FOR XML PATH query
Create function fnConcatMultipleRowValuesToColumn ()
Returns @tab Table (EmpID int,con varchar(200))
As
Begin
DECLARE @Designation TABLE (EmpID INT, Code VARCHAR(50))
INSERT @Designation
SELECT 100, 'SR. Engr.' UNION ALL
SELECT 100, 'TL' UNION ALL
SELECT 100, 'PM' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'QA' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'SR QA' UNION ALL
SELECT 200, 'TL QA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'DBA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'SR. DBA'UNION ALL
SELECT 300, 'TL DBA'
-- Show the expected output
Insert @tab
SELECT DISTINCT s1.EmpID,
STUFF((SELECT DISTINCT TOP 100 PERCENT ',' + s2.CODE FROM @Designation AS s2
WHERE s2.EmpID = s1.EmpID ORDER BY ',' + s2.CODE FOR XML PATH('')), 1, 1, '') AS CODES
FROM @Designation AS s1
ORDER BY s1.EmpID
Return
End
Function Call
Select *From fnConcatMultipleRowValuesToColumn ()
Summary :
Avoid Scalar functions as far as possible. This was introduced in SQL Server 2000 and there may be certain scenario where it may be useful like encapsulation. But when you use scalar function within a select statement which returns many rows may trouble you.
Few good resources to refer
http://sqlblog.com/blogs/adam_machanic/archive/2006/08/04/scalar-functions-inlining-and-performance-an-entertaining-title-for-a-boring-post.aspx
http://www.sqlservercentral.com/Forums/Topic446308-360-1.aspx
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)



